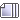
Water in California is shared across three main sectors.
Statewide, average water use is roughly 50% environmental, 40% agricultural, and 10% urban. However, the percentage of water use by sector varies dramatically across regions and between wet and dry years. Some of the water used by each of these sectors returns to rivers and groundwater basins, and can be used again.
Environmental water provides multiple benefits.
Environmental water use falls into four categories: water in rivers protected as "wild and scenic” under federal and state laws, water required for maintaining habitat within streams, water that supports wetlands within wildlife preserves, and water needed to maintain water quality for agricultural and urban use. Most water allocated to the environment does not affect other water uses. More than half of California’s environmental water use occurs in rivers along the state’s north coast. These waters are largely isolated from major agricultural and urban areas and cannot be used for other purposes. In the rest of California where water is shared by all three sectors, environmental use is not dominant (33%, compared to 53% agricultural and 14% urban).



 Poll
Poll